Kubernetes certificate based mutual auth with different CAs
Configuring certificate based mutual authentication in Kubernetes using nginx ingress controller is explained pretty well in this post. However, the post assumes that the certificates used for validating the client and the server are issued by the same CA (Certificate Authority). How do you configure client certificate authentication in kubernetes when using client and server certificates issued by different CAs? The current nginx ingress controller docs do not make this absolutely clear either. I recently came across a scenario where we were using our own internal/private CA for issuing client certificates and a publicly trusted CA for server TLS. This post covers configuring kubernetes nginx ingress to use certificates issued by different CAs on the same host to perform mutual authentication.
What is mutual authentication?
Mutual authentication or 2-way authentication is a process in which both the client and server verify each others identity via a Certificate Authority. An X.509 Certificate can provide identity to a machine or a device and enable the independent verification of the issued identity by an external authority such as a CA. Therefore, mutual authentication as defined by codeproject.com is also referred to as certificate based mutual authentication.
Mutual SSL authentication or certificate based mutual authentication refers to two parties authenticating each other through verifying the provided digital certificate so that both parties are assured of the others’ identity.
You can have the client and the server certificates issued by the same CA or as shown below by different CAs.
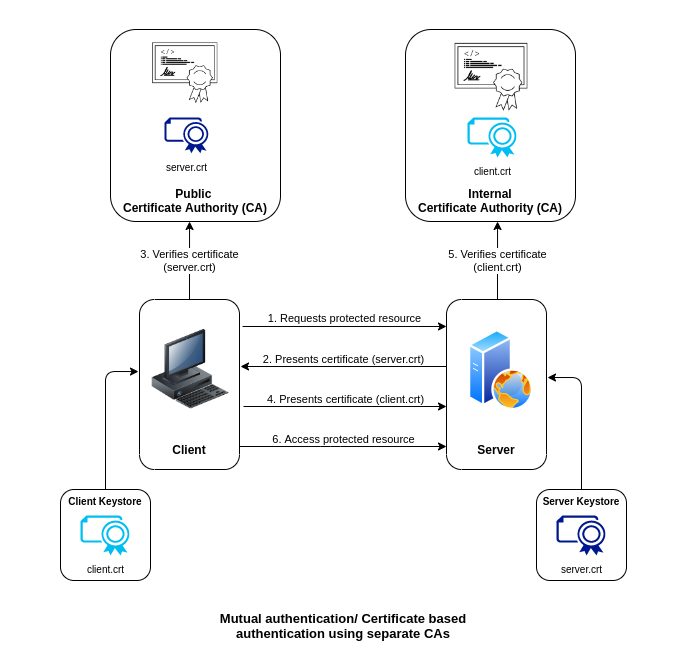
Configuring mutual authentication
In order to configure mutual authentication for a host in a kubernetes cluster, we are going to run a simple application within kubernetes and ensure it can be accessed publicly over TLS only with a valid client certificate.
There are many ways of setting up a kubernetes cluster but for this exercise we are going to use Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS) and deploy nginx ingress controller to it. We use an ingress controller for routing (layer 7) external traffic to your application running within the AKS cluster and exposing multiple services under the same IP address. The ingress controller deployment on AKS provisions a load balancer in Azure and assigns it a public IP. This allows the nginx controller to be accessed publicly via an EXTERNAL_IP. After deploying the nginx ingress controller, you can get its external IP by
kubectl get svc -n ingress-nginx
NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE
ingress-nginx-controller LoadBalancer 10.0.106.200 13.93.79.119 80:31599/TCP,443:31682/TCP 46d
ingress-nginx-controller-admission ClusterIP 10.0.101.201 <none> 443/TCP 46d
We are going to use wildcard DNS service nip.io to give this EXTERNAL_IP a domain name like EXTERNAL_IP.nip.io and configure server TLS for this domain.
Generating the certificates
Usually you are not expected to be in possession of a public CA key and certificate. A Certificate Signing Request (CSR) is sent to a public CA to obtain a globally trusted certificate for securing your assets. However, for demonstration purposes below we will generate two separate CA certificates using OpenSSL and then generate server and client certificates signed by each CA to configure kubernetes ingress.
# Generate a public CA Key and Certificate
$ openssl req -x509 -sha256 -newkey rsa:4096 -days 356 -nodes \
-keyout public-ca.key \
-out public-ca.crt \
-subj '/CN=Public Cert Authority/O=Org Public CA/C=GB'
# Generate the Server Key and Server Certificate and Sign with the public CA Certificate
$ openssl req -new -nodes -newkey rsa:4096 \
-out server.csr \
-keyout server.key \
-subj '/CN={EXTERNAL_IP}.nip.io/O=aks-ingress/C=GB'
$ openssl x509 -req -sha256 -days 365 \
-in server.csr \
-CA public-ca.crt -CAkey public-ca.key \
-set_serial 01 \
-out server.crt
# Generate an internal CA Key and Certificate
$ openssl req -x509 -sha256 -newkey rsa:4096 -days 356 -nodes \
-keyout internal-ca.key \
-out internal-ca.crt \
-subj '/CN=Internal Cert Authority/O=Org Internal CA/C=GB'
# Generate the Client Key and Client Certificate and Sign with the internal CA Certificate
$ openssl req -new -nodes -newkey rsa:4096 \
-out client.csr \
-keyout client.key \
-subj '/CN=internal-client/O=aks-ingress-client/C=GB'
$ openssl x509 -req -sha256 -days 365 \
-in client.csr \
-CA internal-ca.crt -CAkey internal-ca.key \
-set_serial 02 \
-out client.crt
Create the kubernetes secrets
Kubermetes requires you to store the certificates as secrets in order for them to be used by nginx ingress controller. We create 2 separate secrets, one for the internal CA certificate to validate client certificates and the other for server TLS for the client to validate server’s identity.
# Add a secret for the internal CA certificate to validate client certs
kubectl create secret generic internal-ca --from-file=ca.crt=internal-ca.crt
# Add a secret for server TLS (e.g. issued by a public CA) to validate server's identity
kubectl create secret tls server-tls --key server.key --cert server.crt
Deploy the application
- Deploy the application pods.
echo "
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: http-svc
namespace: default
spec:
replicas: 2
selector:
matchLabels:
app: http-svc
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: http-svc
spec:
containers:
- name: http-svc
image: gcr.io/kubernetes-e2e-test-images/echoserver:2.1
ports:
- containerPort: 8080" | kubectl apply -f -
- Expose the pods within the cluster using a Service.
echo "
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: http-svc
namespace: default
spec:
ports:
- port: 80
targetPort: 8080
protocol: TCP
name: http
selector:
app: http-svc" | kubectl apply -f -
Create the ingress rule
The previous step exposes the service within the kubernetes cluster. To access the service externally we need to create an ingress rule. The ingress rule below sets up TLS and makes the service avaialble on https://{EXTERNAL_IP}.nip.io.
default/internal-casecret containing the Internal CA certificate is used for the client certificate validationserver-tlssecret containing the server certificate is used for server TLS
Please note for the ingress rule to take effect it needs to be created in the same namespace as the service.
echo "
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1beta1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-verify-client: \"on\"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-secret: \"default/internal-ca\"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-verify-depth: \"1\"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-tls-pass-certificate-to-upstream: \"true\"
name: http-svc
namespace: default
spec:
rules:
- host: {EXTERNAL_IP}.nip.io
http:
paths:
- backend:
serviceName: http-svc
servicePort: 80
path: /
tls:
- hosts:
- {EXTERNAL_IP}.nip.io
secretName: server-tls" | kubectl apply -f -
Test the ingress configuration
Sending a request without a client certificate and key should give a 400 error, however the server certificate (issued by the Public CA) validation does succeed as shown below
curl -v -k https://{EXTERNAL_IP}.nip.io
* Server certificate:
* subject: CN=13.93.79.119.nip.io; O=aks-ingress; C=GB
* start date: Nov 10 23:19:03 2020 GMT
* expire date: Nov 10 23:19:03 2021 GMT
* issuer: CN=Public Cert Authority; O=Org Public CA; C=GB
...
<center><h1>400 Bad Request</h1></center>
<center>No required SSL certificate was sent</center>
....
Sending a request with the client certificate and key should redirect you to the http-svc:
`curl -v -k https://{EXTERNAL_IP}.nip.io --cert client.crt --key client.key`
...
ssl-client-issuer-dn=C=GB,O=Org Internal CA,CN=Internal Cert Authority
ssl-client-subject-dn=C=GB,O=aks-ingress-client,CN=internal-client
ssl-client-verify=SUCCESS
user-agent=curl/7.58.0
....